Container Orchestration Options with OpenStack Magnum

It's the age of open-source technologies and Cloud Foundry developers eagerly use the variety of them, OpenStack not being an exception. Within that ecosystem, OpenStack Magnum enables the use of containers and there is more than one path that can be taken.
Here, we present some options for those who may be deploying containers with OpenStack and face the choice between native Docker, Kubernetes, or Apache Mesos.
“In 2010, NASA and Rackspace got together as a collaboration and formed the idea of a new software called OpenStack that would allow you to create your own cloud—private or public—at any scale. Since then, we have OpenStack members now at over 27,000, across 167 countries, and over 500 different organizations,” said Rackspace’s during Container World 2016.
Now, five years later, we have OpenStack Magnum, which is the Containers-as-a-Service component for OpenStack. It essentially combines infrastructure software with container software and makes them work together.
To date, OpenStack Magnum is capable of supporting three container orchestration engines (COEs). These COEs are Docker Swarm, Kubernetes, and Apache Mesos.
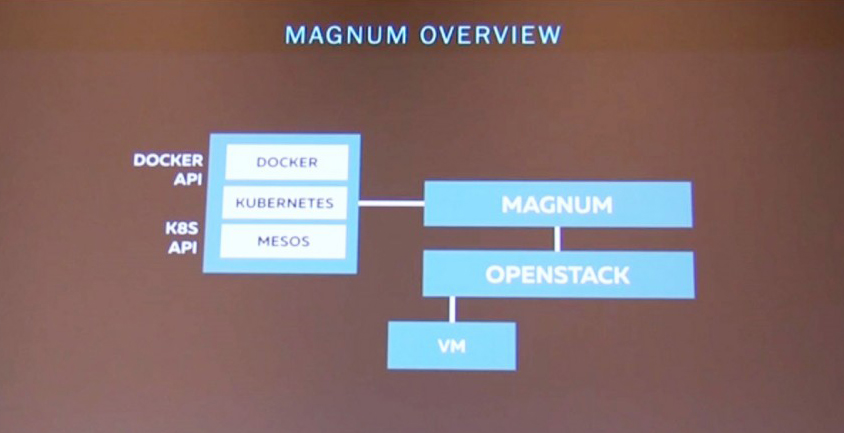
Why use OpenStack Magnum at all?
There’s an argument to be made about simply using any one of the COEs directly and ignoring OpenStack Magnum. Adrian poses the questions, “So why would you care about Magnum at all? Why don’t you just pick one of these COEs and run with it?”
OpenStack Magnum gives you four reasons to use it:
- Choice of COE. As mentioned before, there are three COEs already supported by OpenStack Magnum—Docker Swarm, Kubernetes, and Apache Mesos. In addition to this, Kubernetes support comes with multi-master configuration built-in and Apache Mesos support has the Marathon framework included.
- Secure bays. Generally, a container orchestration system is built out of several components. These components are then accessible through public networks and open up the problem with the lack of authentication and security.
- Load balancer integration. OpenStack Magnum is integrated with Neutron Load-Balancing-as-a-Service (LBaaS) that enables dynamic load balancing regardless of which one of the three COEs are driving the backend.
- Choice of compute type. OpenStack Magnum gives you the choice to run containers on Virtual Machines (VMs) or in Bare Metal configurations.
OpenStack Magnum addresses this problem through the automated TLS certificates. Normally, setting up a distributed system to be secured with the TSL certificates involves multiple configuration steps.

Imperative design vs. declarative design
Before choosing which COE suits your needs, it’s important to note a fundamental difference in the approach of each container orchestration engine. Does the COE use an imperative design or does it use a declarative design? What’s the difference between the two?
An imperative design implies that the system is simple and just does what it’s instructed to do, giving the user total control of the outcome. “In an imperative world, the system itself is totally stupid. It just does what it’s told. All the magic, all the value, all the instructions are provided by the operator. I run a script, I give that script to the system, (and) the system runs the script. That’s an imperative paradigm,” explains Adrian.

On the other hand, a declarative design means that the system is smart—it has all the functions—and the user simply enters a basic command. This system is easier to use but less flexible. “(In) a declarative system, all the smarts are in the system, and the actual input is a very simple statement of what you would like to happen. You have much less control in exactly what happens, but if the system is smart enough and it knows how to do exactly what you want, then this is a much better user experience,” adds Adrian.
With that cleared up, we return to the choice between three COEs supported by OpenStack Magnum: Docker Swarm, Kubernetes, and Apache Mesos.
Why pick Docker Swarm?
- Obviously, if you are already used to the Docker API, Docker Swarm takes the least amount of time getting familiar with. Docker Swarm makes use of the Docker CLI and is compatible with most solutions and technologies already compatible with Docker.
- It has an imperative design with the potential to use declarative tools. If you as a user enjoy having full control of each and every process, Docker Swarm is the way to go. Furthermore, you can use Docker Compose on top of Docker Swarm to add a declarative interface to the already imperative system.
- Docker Swarm allows for a mix-and-match of cloud applications running with legacy (non-cloud) applications in containers.
- You have a large cluster of nodes. If you have thousands of nodes, Docker Swarm scales really well.

Why pick Kubernetes?
- You’re familiar with the Kubernetes API. Kubernetes is developed by Google. Though Kubernetes itself only started in 2014, Google has been in the container development business far longer than anyone else and they know what they’re doing.
- It has a declarative design. While it lacks flexibility, Kubernetes does well within its scope.
- Kubernetes prioritizes cloud applications. This does not necessarily mean that you cannot use legacy applications within Kubernetes. You still can, but it’s not optimal.
- If you have about 200 nodes in your cluster, Kubernetes works great. However, recent updates to Kubernetes, specifically version 1.2, has seen its scaling improve to work well with 1,000 nodes.

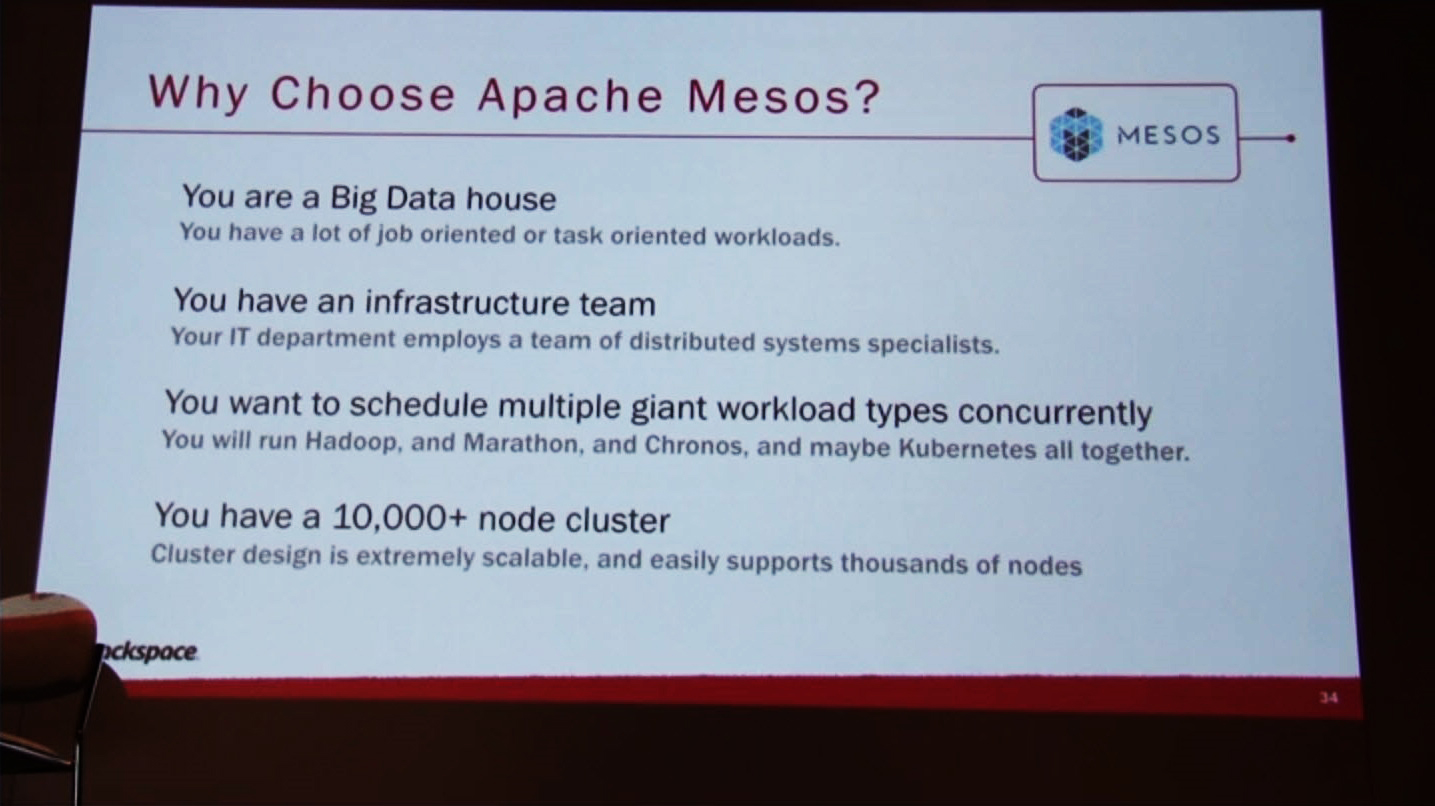
Why pick Apache Mesos?
- Apache Mesos is all about large scale. It’s the ideal choice if you’re into big data.
- You have a dedicated infrastructure team. It’s not easy to look for problems in a giant cluster of nodes, when you don’t have a dedicated infrastructure team.
- Apache Mesos is capable of running multiple workloads all at the same time.
- You have a massive cluster. Apache Mesos is designed to scale for clusters involving thousands upon thousands of nodes.
Obviously, choosing a COE goes far beyond the number of nodes and amount of data. You have to look at your own enterprise’s architecture and requirements and decide from there which fits.
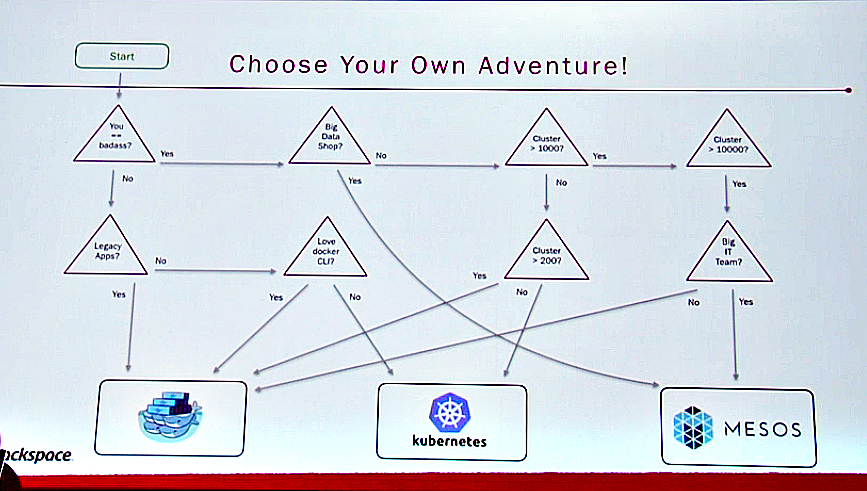
Want details? Watch the video!










